Table of contents
Hello troubleshooters! Machine Learning or ML is one of the most successful applications of Artificial intelligence which provides systems with automated learning without being constantly programmed. It has acquired a ton of noticeable quality lately due to its capacity to be applied across scores of ventures to tackle complex issues quickly and effectively. From Digital assistants that play your music to the products being recommended based on prior search, Machine Learning has taken over many aspects of our life. It is a skill in high demand as companies require software that can grasp data and provide accurate results. The core objective is to obtain optimal functions with less confusion. But in this field, there are also many challenges and difficulties from development to production stages.
Challenges in machine learning is one of the key point which can't be ignored while learning and exploring this domain from scratch because getting an idea of difficulties beforehand makes us prepared to take feasible and robust steps while training models through various algorithms which we'll cover in upcoming part of the series. Till now we have covered topics the scratch do consider checking out previous articles in this on-going series of 100days of machine learning. Let's dig right into the topic:
CHALLENEGES OCCUR DURING HANDLING & TRAINING MACHINE LEARNING MODELS
1. Data collection
Collecting data for training the ML model is the basic step in the machine learning pipeline. The predictions made by ML systems can only be as good as the data on which they have been trained. Following are some of the problems that can arise in data collection:
1.1 Inaccurate data: The collected data could be unrelated to the problem statement.
1.2 Missing data: Sub-data could be missing. That could take the form of empty values in columns or missing images for some class of prediction.
1.3 Data imbalance: Some classes or categories in the data may have a disproportionately high or low number of corresponding samples. As a result, they risk being under-represented in the model.
1.4 Data bias: Depending on how the data, subjects and labels themselves are chosen, the model could propagate inherent biases on gender, politics, age or region, for example. Data bias is difficult to detect and remove.
2. Insufficient data/ labelled data
The real problem with insufficient data lies in the fact that with less data, variance increases. Variance, which can easily be defined as the variability of model prediction for a given data point or a value which tells us how the data is spread. High variability in models, means that the model will fit the training data perfectly, but will stop working as soon as new data is fed into it.
3. Non representative training data
In order to generalize the model well, it is crucial that the training data be an accurate representation of the population. In other words, each time a new sample is derived from the population, it is crucial that the sample must accurately paint a picture of the population. A training set of data must be representative of the cases you want to generalize to. It is, however, harder than it sounds. If the sample is too small, you will have sampling noise, which is the nonrepresentative data as a result of chance, but even large samples can be nonrepresentative if the sampling method is flawed. This is called Sampling Bias.
4. Poor quality data
Data quality is a pre-condition for AI, and not the other way around! Meaning, if the quality of your data is bad, analytics and Ai initiatives are worthless to pursue.
5. Irrelevant features
Feature Selection is one of the core concepts in machine learning which hugely impacts the performance of your model. The data features that you use to train your machine learning models have a huge influence on the performance you can achieve. Garbage In Garbage Out rightly said when it comes to train machine learning model. By the way, with the help of Feature engineering we remove irrelevant features.
6. Overfitting
Overfitting & underfitting are the two main errors/problems in the machine learning model, which cause poor performance in Machine Learning.
Overfitting occurs when the model fits more data than required, and it tries to capture each and every datapoint fed to it. Hence it starts capturing noise and inaccurate data from the dataset, which degrades the performance of the model.
An overfitted model doesn't perform accurately with the test/unseen dataset and can’t generalize well.
An overfitted model is said to have low bias and high variance.
7. Underfitting
Underfitting is a phenomenon in machine learning where the training set does not learn the important parameters for predictions on the test set.
A model that has a high bias (underfitting) is likely going to give a high error value on the test set and also the training set. One of the things to note is that when we take a complex model, there would be a lesser chance for it to underfit as those parameters learn important information.
On the other hand, models that are less complex would have a higher bias or would underfit the data.
8. Software integration
A scalable production environment that is well integrated with different datasets and modeling technologies is crucial for the ML model to be successful. Integrating different teams and operational systems is always challenging.
Complicated codebases have to made into well-structured systems ready to be pushed into production. In the absence of a standardized process to take a model to production, the team can get stuck at any stage.
Workflow automation is necessary for different teams to integrate into the workflow system and test. If the model isn’t tested at the right stage, the entire ecosystem would have to be fixed at the end. Technology stacks have to be standardized else integration could be a real nightmare.
Integration is also a crucial time to make sure that the Machine Learning experimentation framework isn’t a one-time wonder. Else if the business environment changes or during a catastrophic event, the model would cease to provide value.
9. Offline learning/ deployment
The first thing that we should understand is that there are huge differences between developing an ML model and deploying one. These differences translate into huge discrepancies in terms of performance, speed, and resource consumption.
All tasks and priorities should be subordinated to the constant monitorization of the ML model deployed, the application should have the best version to be in production to serve live requests from users.
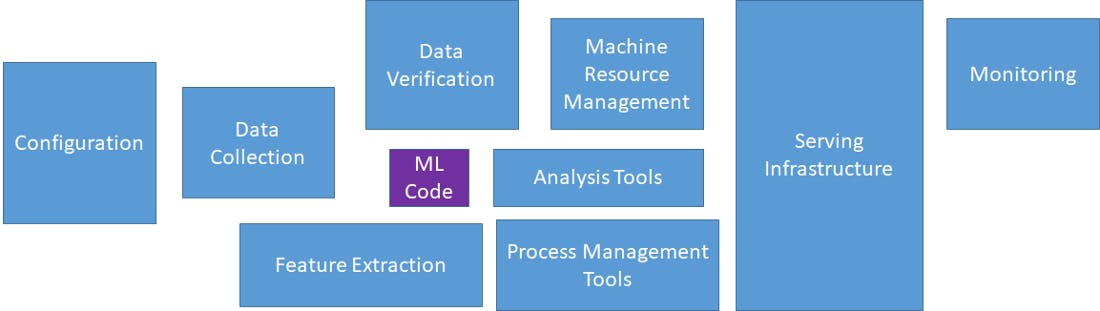
And, in practice, the role of the ML code in the overall deployment in production is a very small portion of the entire structure needed for it to work correctly. Something in the order shown in the following figure:
 ext
ext
Hidden Technical Debt in Machine Learning Systems — Image reproduced by the author Stakeholder Coordination Usually, the most common issue in any ML model deployment is to coordinate the deployment team with other team members who lack machine learning knowledge or understanding.
Model deployment is a group task that needs constant communication and a common understanding of the overall objective. An adequate plan at the early stages of ML model development is key for the MLOps/DevOps team to prepare well for the deployment.
Programming Language Discrepancies
Normally, the ML model is developed in Python or some variation such as TensorFlow or PyTorch, and the application that uses its output is developed in Java, C++, or Ruby. Although nowadays is becoming easier and easier to migrate the ML models to integrate smoothly with the application, programming discrepancy brings some integration challenges to the table.
Model Drift
Model drift is the decrease of the performance of the ML model below the specified benchmark/threshold. This is why is so important to constantly monitor the ML model performance, to be able to detect and update the model to have the best version available online and running.
This performance decrease is often produced by:
Changing behavior of the data: due to the dynamic nature of data, it and its inner patterns may change across time. So one ML model performing very well at its deployment will see how its performance decrease across time as the patterns and the adjustment of its inner weights are no longer mirroring current data. In these cases, the model must be retrained with the most actual data and move the new version into production.
Changing interpretation of the New Data: This is due to a concept drift and usually, it appears because of a change of the interpretation of a certain label or category. For example, some groups of clients may be characterized to belong to group X and at one point in time, the business decides to change it to class Y. Again, the model will be no longer useful and needs to be retrained and put back into production.
On-Premise vs Cloud-Based Deployment
Both approaches have their own pros and cons and are more suitable depending on the problem trying to solve. So the business, along with the Data Science team, need to analyze and decide which implementation is best.
Clear Ownership
Each member of the team has to clearly know his/her responsibilities and role. Usually, DevOps does not know much about what is going on under the model’s hood and need a deep enough explanation of its behavior to integrate it correctly in the application. On the other hand, Data Scientists tend to assume that their job is done when the model is developed. So it is key the fluent communication across the entire team to ensure that the deployment is done in the required time, cost, and quality and to avoid any potential issues.
Model Performance Monitoring
The monitoring strategy needs to be planned before putting the model into production and normally it will be designed around the following questions:
When to retrain the model?
How much data will be used to retrain the model?
What is the performance threshold for the model?
Version Management
This is a key aspect to consider. It helps to:
Track which model is the best
The different file dependencies
Data resources pointers
Git is the most spread way to track versions and staged deployment.
Privacy-Preserving and Secure Model
This topic is one of the most important ones. It is key to safely secure the model so no adversarial attack could expose its data to third parties.
10. Cost involved
The hardest part about deploying ML models correctly can be convincing others to make a larger investment today in order to establish a long-term pattern of success. Here are a few things to keep in mind:
Direct focus towards the long-term vision and not the short-term cost. That’s easier said than done given the typical enterprise budgeting processes, but try to present costs in the context of protecting the investment you’ve already made in machine learning by giving it the highest possible chance of success.
For unforeseen costs, remember that following best practices today will ensure that no one inadvertently ends up in a tech dead-end situation tomorrow.
Remember that the overall goal is building up a portfolio of ML projects for true digital transformation; whenever possible, present costs in terms of dollars required to add a model to the system as opposed to the absolute cost of deploying the first model. Talk about the TCO per model once 5, 10, or 50 models have been deployed to highlight the value of building scalable systems.
That's all about the major challenges in the filed of machine learning adjourning this article now. In the upcoming article node we would be exploring about the applications of machine learning in our day to day stuff. Till then signing off!
Read till here thanks a bunch:)

