Hello troubleshooters! this article is under on going series 100days of machine learning do consider checking out previous articles I have explained the whole machine learning from the scratch. In today's article the whole focus would be centric around ONLINE MACHINE LEARNING , let's begin on that note:
WHAT ACTUALLY IS ONLINE LEARNING?
In online learning, you train the system incrementally by feeding it data instances sequentially, either individually or by small groups called mini-batches. Each learning step is fast and cheap, so the system can learn about new data on the fly, as it arrives. For example chatbots of social media platforms , YouTube content recommendation system is a perfect example of online learning.
Online learning is great for systems that receive data as a continuous flow (e.g., stock prices) and need to adapt to change rapidly or autonomously. It is also a good option if you have limited computing resources: once an online learning system has learned about new data instances, it does not need them anymore, so you can discard them (unless you want to be able to roll back to a previous state and “replay” the data). This can save a huge amount of space.
Online learning algorithms can also be used to train systems on huge datasets that cannot fit in one machine’s main memory (this is called out-of-core learning). The algorithm loads part of the data runs a training step on that data and repeats the process until it has run on all of the data.
WHEN TO USE ONLINE LEARNING?
- When there is a concept drift (The term “concept drift” refers specifically to the accuracy of the model. Data drift is a phenomenon where the data underlying the model has changed significantly)
- Cost effective
- Faster solution
LEARNING RATE
In machine learning and statistics, the learning rate is a tuning parameter in an optimization algorithm that determines the step size at each iteration while moving toward a minimum of a loss function. Since it influences to what extent newly acquired information overrides old information, it metaphorically represents the speed at which a machine learning model "learns" .
OUT OF CORE LEARNING
Out-of-core learning refers to a set of algorithms working with data that cannot fit into the memory of a single computer, but that can easily fit into some data storage such as a local hard disk or web repository.
DISADAVANTAGES OF ONLINE LEARNING
- Tricky to use
- Risky
BATCH Vs ONLINE LEARNING
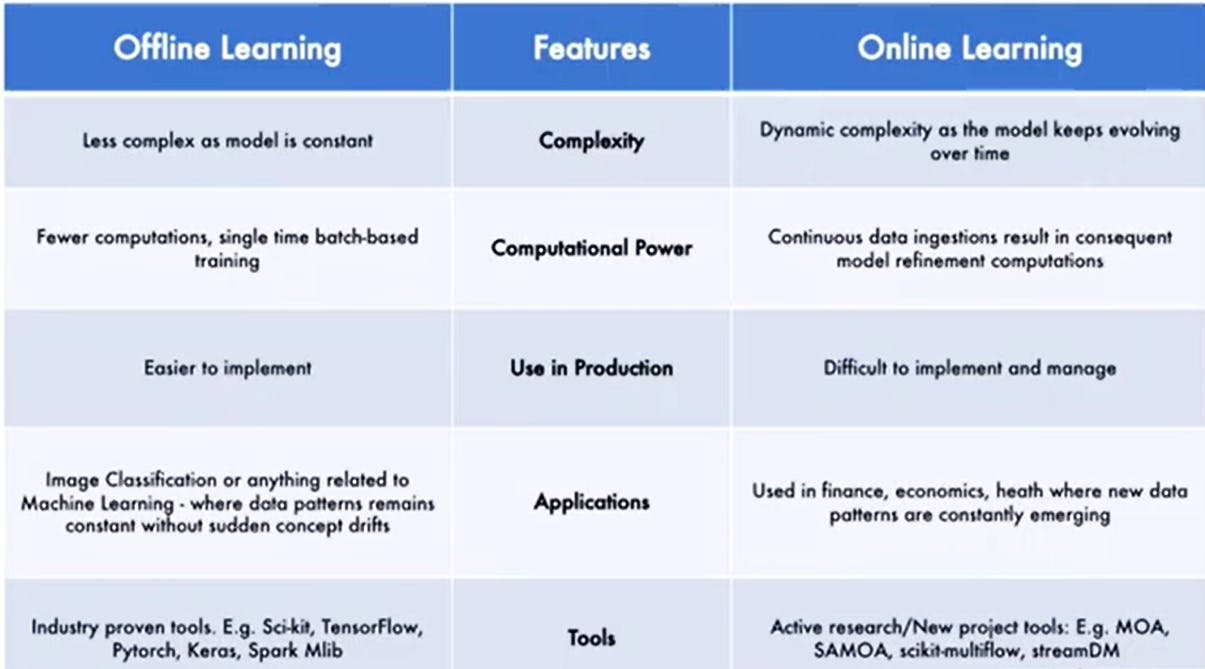
So yeah that's all for this article specific here we are done with the classification part of the training models at production level. Now in the upcoming part of this series we would exploring machine learning on the basis of its learning methods.
Read till here thanks a bunch:)

